Types of blepharitis and causes
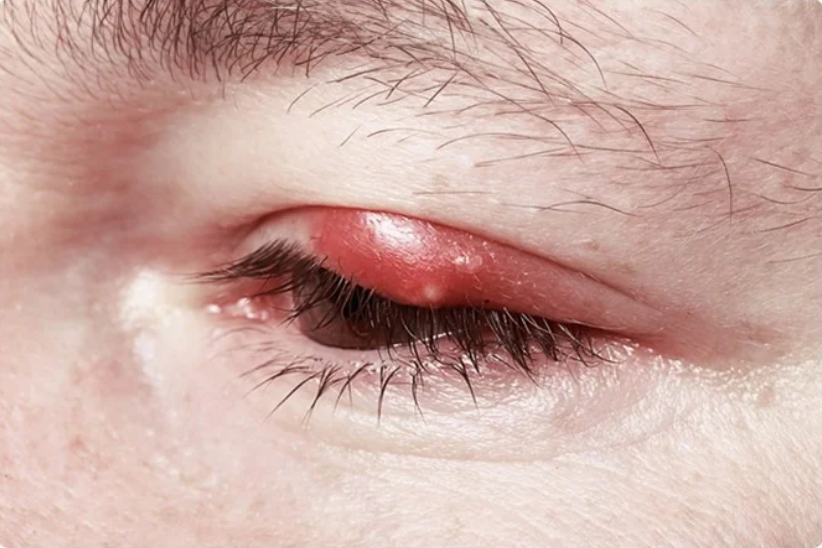
Blepharitis, a common eye illness, is a condition where the eyelids are visibly inflamed.
The discomfort brought on by bacteria makes the eyelids itch and turn red. Patients who have blepharitis experience discomfort, despite the fact that it does not permanently harm their vision. Meibomian gland dysfunction is more common in women who are peri- and postmenopausal.
Types of blepharitis There are three different types of blepharitis: anterior, posterior, and mixed.
The epidermis, base, and follicles of the eyelashes are all impacted by anterior blepharitis. The inner margin of the eyelid closest to the eyeball develops posterior blepharitis. Mixed blepharitis is the term used to describe blepharitis that affects some patients with both anterior and posterior kinds.
anterior blepharitis causes
The main causes of anterior blepharitis are staphylococcal infections or seborrheic dermatitis.
infections with Staphylococcus
Staphylococcal blepharitis causes symptoms like somewhat sticky eyelids, larger eyelid borders, and lost eyelashes.
Despite the fact that Staphylococcus bacteria are frequently found in the skin, nose, buttocks, and surface of the armpits, they can still enter the human body through cuts, insect bites, or skin openings made while using medical devices like urinary catheters.
From simple skin and soft tissue infections to invasive infections known as Staphylococcal infections or staph infections, the bacteria Staphylococcus is the cause of a variety of illnesses. One of the many Staphylococci species is methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), which has become resistant to several medications, including flucloxacillin, a medication frequently used to treat staph infections. The most common cause of infections is the staphylococcus aureus strain Panton-Valentine leukocidin (PVL), which produces a toxin called PVL that can damage white blood cells and cause recurrent skin infections.
Why do eating disorders occur?
Infections can afflict healthy people, but those with weakened immune systems, such as chemotherapy patients, are more vulnerable to them.
Dermatitis seborrheic
Eczema of the sort known as seborrhoeic dermatitis can be seen in areas where the sebaceous glands are active. It is said that the yeast Malassezia furfur causes seborrheic dermatitis to flare up. The severity of eczema, however, is unrelated to sebum production.
Despite having a higher sebum production, some people do not have eczema. Seborrhoeic dermatitis is risky due to illnesses like depression, epilepsy, excessive alcohol use, and drugs like psoralen, lithium, and interferon, even if the precise origin of the disorder is not fully understood.
Blepharitis may result from metabolites like decreased fatty acid levels or a rise in oleic acid, cholesterol, and/or triglyceride levels. Seborrheic dermatitis manifests as symptoms include red eyelid borders with scaly edges.
posterior blepharitis causes
Issues with the interior of the eyelid are related to posterior blepharitis. Meibomian glands, which are tiny oil glands, are located along the eyelid edges. Each eyelid has between 15 and 20 of these glands, which are located in both the lower and upper eyelids.
The meibomian gland apertures are normally found on the margins of the eyelids, inside the eyelash line. When the eyes are closed, the oil slowly percolates, but when the gland is empty, it collapses.
A tear film is formed when the oil produced by this gland combines with the watery component of the eye. The water layer is coated by this oily layer, which also shields it from evaporation. Eye irritation is one of the symptoms that may appear when the quantity or quality of the water or oil is altered.
Meibomian blepharitis can be identified by symptoms like redness on the inside of the eyelids and poor tear quality. This is due to the eyelid glands’ inconsistent oil production, which also encourages bacterial growth. The bacteria break down the meibomian gland secretions, which can irritate the eye while also giving the tear film a frothy appearance. There will be inflammation and the development of crusty flakes as a result of the extra oil that forms along the edge of the eyelid.
The meibomian gland slits may get blocked by eyelid border inflammation. Due to the obstruction, less oil will be produced, which will result in thickened and tainted oil remaining in the gland.
What causes malfunction of the meibomian glands?
The meibomian glands can become dysfunctional for a variety of reasons, but rosacea is one skin condition that can prevent the meibomian gland from working properly.
Patients with rosacea have higher concentrations of the species Demodex folliculorum, which is present in both meibomian glands and hair follicles. These species may accumulate excessively and trigger the immune system, resulting in ocular rosacea. In addition to producing discomfort in the eyes of affected people, ocular rosacea causes the eyes of many rosacea sufferers to appear red or watery.
Blepharitis is brought on by the two species of microscopic mites in the Demodex genus. Demodex brevis causes posterior blepharitis and Demodex folliculorum causes anterior blepharitis. In addition to causing direct damage, the Demodex mite also transmits the bacteria Staphylococci, which can result in Staphylococcal illnesses.